Difference between revisions of "LipidXplorer Reference"
m (1 revision imported) |
|||
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
Shotgun spectra datasets mostly consist of survey MS spectra and full MS/MS spectra acquired either from peaks detected in survey spectra, or from peaks whose masses matched the masses from a pre-compiled inclusion list. This is called data dependent acquisition (DDA). Although data-dependent acquisition is a powerful approach it is most efficient on rapid high mass resolution tandem instruments such as hybrid quadrupole time-of-flight or LTQ Orbitrap mass spectrometers. | Shotgun spectra datasets mostly consist of survey MS spectra and full MS/MS spectra acquired either from peaks detected in survey spectra, or from peaks whose masses matched the masses from a pre-compiled inclusion list. This is called data dependent acquisition (DDA). Although data-dependent acquisition is a powerful approach it is most efficient on rapid high mass resolution tandem instruments such as hybrid quadrupole time-of-flight or LTQ Orbitrap mass spectrometers. | ||
| − | ===Precursor ion scan (PIS) or neutral loss scan (NLS) data=== | + | ===Precursor ion scan (PIS) or neutral loss scan (NLS) data; removed in LipidXplorer 1.2.8=== |
A large body of lipidomics work is performed by triple quadrupole or triple quadrupole - linear ion trap (QTRAP) mass spectrometers. In this way, no full MS/MS spectra are acquired: the instrument is set to detect one specific fragment originating from all precursors masses within a specified m/z range. In each analysis, the fragment mass (in case of PIS) or mass difference (in case of NLS) is monitored and then the analysis is repeated for the next fragment mass / mass difference of interest. This analysis produces a differently structured dataset | A large body of lipidomics work is performed by triple quadrupole or triple quadrupole - linear ion trap (QTRAP) mass spectrometers. In this way, no full MS/MS spectra are acquired: the instrument is set to detect one specific fragment originating from all precursors masses within a specified m/z range. In each analysis, the fragment mass (in case of PIS) or mass difference (in case of NLS) is monitored and then the analysis is repeated for the next fragment mass / mass difference of interest. This analysis produces a differently structured dataset | ||
PIS data has a different structure compared to DDA data. This is explained in more detail with the following figure. | PIS data has a different structure compared to DDA data. This is explained in more detail with the following figure. | ||
| − | ===DDA vs. PIS/NLS=== | + | ===DDA vs. PIS/NLS; removed in LipidXplorer 1.2.8=== |
[[File:Comparison-DDA_vs_PIS.png|600px|right]] | [[File:Comparison-DDA_vs_PIS.png|600px|right]] | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
''LipidXplorer provides automatic conversation of data from ThermoFinnigan (Orbitrap) and Applied Biosystems (QStar) provided that the instruments software is installed on the same computer as LipidXplorer.'' | ''LipidXplorer provides automatic conversation of data from ThermoFinnigan (Orbitrap) and Applied Biosystems (QStar) provided that the instruments software is installed on the same computer as LipidXplorer.'' | ||
| − | ==== Import of peak lists of MS/MS in *.dta format and MS in *.csv ==== | + | ==== Import of peak lists of MS/MS in *.dta format and MS in *.csv; removed in LipidXplorer 1.2.8==== |
As an easy way to make the functionality of LipidXplorer available for a wide range of mass spectrometric platforms is to provide the ability to import pre-processed peak-lists. Many vendors enable the functionality in their software to create *.dta files of MS/MS Spectra. In many instances one might be interested to import also the pre-processed peaklist of the MS1 which we support with the widely used *.csv file format. Both text file formats should be reasonable available as alternative for *.mzXml. For the import of *.dta and *.csv files, some pre-conditions have to met: The import files have to be given in a certain directory structure, which is: | As an easy way to make the functionality of LipidXplorer available for a wide range of mass spectrometric platforms is to provide the ability to import pre-processed peak-lists. Many vendors enable the functionality in their software to create *.dta files of MS/MS Spectra. In many instances one might be interested to import also the pre-processed peaklist of the MS1 which we support with the widely used *.csv file format. Both text file formats should be reasonable available as alternative for *.mzXml. For the import of *.dta and *.csv files, some pre-conditions have to met: The import files have to be given in a certain directory structure, which is: | ||
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
The names of the samples occurring in LipidXplorer are the names of the sample directories. | The names of the samples occurring in LipidXplorer are the names of the sample directories. | ||
| − | ===== Import of MS1 information using *.csv file format | + | ===== Import of MS1 information using *.csv file format; removed in LipidXplorer 1.2.8===== |
A *.csv file is a comma separated file, i.e. every line in the file contains data which is separated by commas. LipidXplorer will solely recognize *.csv files for importing survey scan information(the MS experiment data) in the following format: | A *.csv file is a comma separated file, i.e. every line in the file contains data which is separated by commas. LipidXplorer will solely recognize *.csv files for importing survey scan information(the MS experiment data) in the following format: | ||
| Line 78: | Line 78: | ||
705.5908,35523.1 | 705.5908,35523.1 | ||
706.5044,107847.3 | 706.5044,107847.3 | ||
| − | </pre> | + | </pre> |
| − | ===== Import of MS/MS spectra using *.dta ===== | + | |
| + | ===== Import of MS/MS spectra using *.dta;removed in LipidXplorer 1.2.8 ===== | ||
Many mass spectrometers software are able to generate a peak lists of MS/MS spectra and save them in the *.dta file format. It contains a peak list table, which has as head the precursor mass in m/z and its charge and the tables content are masses with the according intensity. | Many mass spectrometers software are able to generate a peak lists of MS/MS spectra and save them in the *.dta file format. It contains a peak list table, which has as head the precursor mass in m/z and its charge and the tables content are masses with the according intensity. | ||
| Line 127: | Line 128: | ||
The tab contains various possibilities of specifying mass spectrometric attributes. The configurations are stored in an *.ini file. There is a standard *.ini file provided, but by pressing 'Browse' next to the *.ini file, the user can select an own file. | The tab contains various possibilities of specifying mass spectrometric attributes. The configurations are stored in an *.ini file. There is a standard *.ini file provided, but by pressing 'Browse' next to the *.ini file, the user can select an own file. | ||
| − | ====Importing PIS/NLS==== | + | ====Importing PIS/NLS; removed in LipidXplorer 1.2.8==== |
Importing PIS/NLS spectra is done by checking "PIS spectra" on the Import Source panel of LipidXplorer. If this is not checked the spectra are not imported properly. | Importing PIS/NLS spectra is done by checking "PIS spectra" on the Import Source panel of LipidXplorer. If this is not checked the spectra are not imported properly. | ||
| Line 153: | Line 154: | ||
'''resolution:''' the resolution of the mass spectrometer in MS and MS/MS mode. | '''resolution:''' the resolution of the mass spectrometer in MS and MS/MS mode. | ||
*This value is used in the import for the spectra averaging and alignment. Both algorithms consider m/z values as equal if they are closer than the resolution allows. | *This value is used in the import for the spectra averaging and alignment. Both algorithms consider m/z values as equal if they are closer than the resolution allows. | ||
| − | + | *Value given here defines resolution at the smallest m/z value of a give m/z range. Resolution will be computed according to slope given in "resolution gradient". | |
'''tolerance:''' The tolerance value is the error LipidXplorer allows for a lipid to be identified. | '''tolerance:''' The tolerance value is the error LipidXplorer allows for a lipid to be identified. | ||
Latest revision as of 13:19, 1 October 2019
The acquisition format
The standard format of data dependent acquisition
Shotgun spectra datasets mostly consist of survey MS spectra and full MS/MS spectra acquired either from peaks detected in survey spectra, or from peaks whose masses matched the masses from a pre-compiled inclusion list. This is called data dependent acquisition (DDA). Although data-dependent acquisition is a powerful approach it is most efficient on rapid high mass resolution tandem instruments such as hybrid quadrupole time-of-flight or LTQ Orbitrap mass spectrometers.
Precursor ion scan (PIS) or neutral loss scan (NLS) data; removed in LipidXplorer 1.2.8
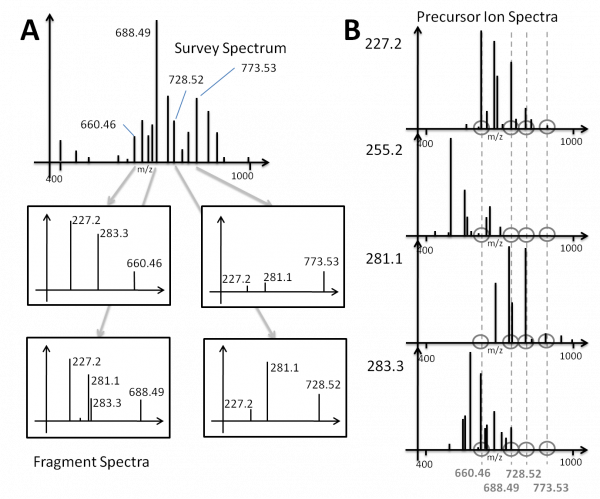
A large body of lipidomics work is performed by triple quadrupole or triple quadrupole - linear ion trap (QTRAP) mass spectrometers. In this way, no full MS/MS spectra are acquired: the instrument is set to detect one specific fragment originating from all precursors masses within a specified m/z range. In each analysis, the fragment mass (in case of PIS) or mass difference (in case of NLS) is monitored and then the analysis is repeated for the next fragment mass / mass difference of interest. This analysis produces a differently structured dataset PIS data has a different structure compared to DDA data. This is explained in more detail with the following figure.
DDA vs. PIS/NLS; removed in LipidXplorer 1.2.8
DDA-driven MS/MS and Precursor Ion Scan (PIS) Spectra. The scheme explains how data-dependent acquisition of full MS/MS spectra (DDA-driven MS/MS) and precursor ion spectra are interrelated. In DDA mode (A) a tandem mass spectrometer first acquires a survey spectrum presenting masses of intact lipids and then fragments all detectable precursors (here we took m/z 660.46; 688.49; 728.52 and 773.53 as an example) to acquire full MS/MS spectra (with an m/z range from the lowest expected fragment to the m/z of the intact precursor). Hence, a dataset of MS/MS spectra comprising all fragment ions generated from all detectable precursors is produced. In the MS/MS spectra (panel A) we designated m/z of characteristic acyl anion fragments (m/z 227.2; 281.1; 283.3) produced from fatty acid moieties in molecular anions of glycerophospholipids. When operating in precursor ion scanning (PIS) mode, (B) the mass spectrometer registers the intensity of one pre-selected fragment (in our example, the same acyl anion) produced from all masses within m/z range of precursors. In this mode, only precursors producing the specific fragment will produce a peak, while others not. Usually, on most common triple quadrupole mass spectrometers PIS spectra are acquired successively for a large number of fragments (like, all acyl anions of major fatty acids) . Then these spectra could be aligned to reveal what fragments out of the expected pool were produced from a particular precursor (dotted line). For example, the lipid with m/z 660.46 produced acyl anions with m/z 227.2 and 283.3 that correspond to 14:0 and 18:0 fatty acids. At the same time, fragments other than from the pre-selected set, will remain undetected. The scheme exemplifies that DDA-driven MS/MS and PIS produce complementary structural evidence, although they originate from two completely different modes of spectra acquisition.
LipidXplorer Import
Supported file formats
*.mzML
mzXML is a XML (eXtensible Markup Language) based common file format for mass spectrometric data Deutsch EW (2008). "mzML: A single, unifying data format for mass spectrometer output". Proteomics 8 (14): 2776–7.. It should replace the commonly used file formats *.mzData and *.mzXML. See Wikipedia on mass spectrometry data formats for more information.
*.mzXML
mzXML is a XML (eXtensible Markup Language) based common file format for mass spectrometric data. [Pedrioli PG et al., Nat. Biotechnol. 22 (11): 1459, 66 doi) (Lin SM et al., Expert review of proteomics 2 (6): 839, 45, PMID)
LipidXplorer provides automatic conversation of data from ThermoFinnigan (Orbitrap) and Applied Biosystems (QStar) provided that the instruments software is installed on the same computer as LipidXplorer.
Import of peak lists of MS/MS in *.dta format and MS in *.csv; removed in LipidXplorer 1.2.8
As an easy way to make the functionality of LipidXplorer available for a wide range of mass spectrometric platforms is to provide the ability to import pre-processed peak-lists. Many vendors enable the functionality in their software to create *.dta files of MS/MS Spectra. In many instances one might be interested to import also the pre-processed peaklist of the MS1 which we support with the widely used *.csv file format. Both text file formats should be reasonable available as alternative for *.mzXml. For the import of *.dta and *.csv files, some pre-conditions have to met: The import files have to be given in a certain directory structure, which is:
MasterScan Dir/
|
|
------------------------------------------------------
| | |
| | |
[neg_]Sample1/ [neg_]Sample2/ ... ... ... [neg_]SampleN/
| | |
/\ | /\
[*.csv], /\ [*.csv],
[*.dta1, *.dta2, ...] [*.csv], [*.dta1, *.dta2, ...]
[*.dta1, *.dta2, ...]
The top level directory defines which samples go into the MasterScan database object. This are namely all samples occurring as subdirectories.
A sample directory can contain either
1. a .csv file with the MS data
2. a .dta files with the MS/MS data
MS precursor intensities are set to a) 1 - when *.dta with this precursor is present b) 0 - when no *.dta with this precursor m/z was found in a sample
3. one .csv file with the MS data and a number of .dta files containing MS/MS data
IMPORTANT! In the names of the sub-directory folders it should be ciphered if its the data is obtained in positive or in negative mode. This is done as follows:
- if a directory has 'neg' at the beginning of its name, the according sample is negative.
- if a directory has 'pos' at the beginning of its name, the according sample is positive.
The names of the samples occurring in LipidXplorer are the names of the sample directories.
Import of MS1 information using *.csv file format; removed in LipidXplorer 1.2.8
A *.csv file is a comma separated file, i.e. every line in the file contains data which is separated by commas. LipidXplorer will solely recognize *.csv files for importing survey scan information(the MS experiment data) in the following format:
/precursor mass/, /intensity/
The *.csv is utilized for representing the (precursor-)mass spectrum. For example - a section of a *.csv file:
701.4101,20952.3 701.5598,4284.7 702.4135,6333 702.5435,23323.7 703.547,7105.8 703.5752,218373.4 704.5786,81777.7 705.5009,253758 705.528,18535.5 705.5822,8314.5 705.5908,35523.1 706.5044,107847.3
Import of MS/MS spectra using *.dta;removed in LipidXplorer 1.2.8
Many mass spectrometers software are able to generate a peak lists of MS/MS spectra and save them in the *.dta file format. It contains a peak list table, which has as head the precursor mass in m/z and its charge and the tables content are masses with the according intensity.
/mass/ /intensity/
For example - the content of a *.dta file of the precursor mass 585.9765 with charge +1:
585.9765 1 197.32957 33132.1 197.33095 12631.7 568.45007 241767.3 569.29065 14319.8
Mass spectrometry file converters
Only a few mass spectrometers directly produce mzXML/mzML files but there are several tools available that generate mzXML/mzML files from native acquired files.
The currently most featured converter is MSConvert, a side project of the ProteoWizard software. It is constantly maintained to support various vendor file formats:
- Agilent Mass Hunter Data Access Component Library
- Waters Raw Data Access Component Library
- Bruker CompassXtract
- Thermo-Scientific MSFileReader Library
- Waters Raw Data Access Component Library
- AB Sciex WIFF Reader Library
Other available converters are:
- for Thermo Scientific Xcalibur *.raw files: ReAdW,
- for Waters MassLynx *.raw filesMassWolf and
- for Sciex/ABI Analyst *.wiff files mzWiff.
Importing mass spectra into LipidXplorer
LipidXplorer only imports spectra which are given as centroid (m/z, intensity pairs). Make sure that your spectra data is not in profile mode.
All spectra which should be put in one MasterScan (see #The_MastersScan_database) should also be in one folder. The folder is the information which is given to LipidXplorer to import the spectra.
If the spectra are given in *.csv/*.dta file format, follow the instructions given in #Import_.2A.dta_.2F_.2A.csv_files. Also here, the folder where all the peak lists are contained is the input for the LipidXplorer import.
Choose the folder with your mass spectral data by clicking the green 'Browse' button or drag the folder into the text field with your mouse. LipidXplorer will fill the fields for the target MasterScan file automatically. To change this press 'Browse' next to the file.
Select a machine specific configuration from the Select configuration list, edit the settings and store them in the configuration file.
The import starts with pressing 'Start import'.
The tab contains various possibilities of specifying mass spectrometric attributes. The configurations are stored in an *.ini file. There is a standard *.ini file provided, but by pressing 'Browse' next to the *.ini file, the user can select an own file.
Importing PIS/NLS; removed in LipidXplorer 1.2.8
Importing PIS/NLS spectra is done by checking "PIS spectra" on the Import Source panel of LipidXplorer. If this is not checked the spectra are not imported properly.
Machine specific settings
selection window: describes the size of the isolation window which is used by the mass spectrometer to select the precursor for fragmentation. Note: The size of the selection window is half of the total instrumental isolation window used:
- The size of a given selection window w of a peak p is [p - w, p + w].
The value w has to be given in Dalton.
timerange: defines time window for all spectra which should be imported.
It is a tuple with (start time, end time) with the time is given in seconds.
calibration masses: a list of standard masses can be given here, which are used for a linear offset correction in MS and MS/MS spectra.
- The standard masses are searched in the spectra within an allowed error given in tolerance. If found, the mass error is used to calculate and apply a mass shift through the whole spectrum.
- If more than one mass is given, a linear function connects the shift values.
massrange: restrict the imported masses.
This helps to decrease import time, resources the speed of lipid identification.
resolution: the resolution of the mass spectrometer in MS and MS/MS mode.
- This value is used in the import for the spectra averaging and alignment. Both algorithms consider m/z values as equal if they are closer than the resolution allows.
- Value given here defines resolution at the smallest m/z value of a give m/z range. Resolution will be computed according to slope given in "resolution gradient".
tolerance: The tolerance value is the error LipidXplorer allows for a lipid to be identified.
- The unit can be either parts per million (ppm) or Dalton (Da).
threshold: is the required minimum intensity for a peak to to be in the MasterScan.
- LipipXplorer offers to input the threshold value as relative or absolute. The relative threshold has to be given in % and is the percentage of the base peak intensity - the highest peak in the spectrum. The base peak for the relative threshold used for the aligned spectra is the highest base peak of all imported spectra. NOTE: In MS/MS the relative threshold can only be used for PIS/NLS acquired spectra. The reason is the diversity of MS/MS spectra in DDA mode - some precursors might be high abundant, some might be low abundant. The danger is that low abundant lipid species might be lost due to a strong difference to high abundant peaks. This is especially true for isobaric species, where high and low abundant species are in the same MS/MS.
- LipidXplorer corrects the threshold value by dividing it with the square root of the number of scans in the given mass spectra time segment. This is due to the increase of information with more scans. The central limit theorem is the model behind this correction.
- NOTE: Be aware that the intensity values may be different in your mzXML file than in your mass spec software (like Analyst or Xcalibur)! Note that for the threshold value the peak intensity is read from the mzXML file and not from the original .wiff or .raw files. All the other peaks below threshold are dismissed.
min occupation: it states the minimum relative number of acquisitions where a mass has to occur.
- For example: a min occupation of 0.5 states, that each ion should be present in at least 50% of all samples.
resolution gradient: is the gradient of the machines resolution in MS and MS/MS mode.
- E.g., a value of -78.5 means that the resolution decreases about 78.5 with every increase of 1 m/z. This simulates a typical behavior of mass spectrometers. The resolution decreases with higher masses.
- On Orbitrap machines we discovered a decrease of 50,000 from m/z 300 to m/z 1200. This gradient value increases the accuracy of the spectra alignment.
MS1 offset: All MS1 m/z values will be shifted by this value.
- The value has to be given in Da.
PMO: The Precursor Offset Correction (PMO) (mainly a correction function for Orbitrap instruments).
- This value shifts m/z values of the precursors from the fragment spectra. The direction of the shift is given by a positive or negative prefix. The prefix is always the opposite of what was set for the acquisition in the Orbitrap.
- NOTE: This offset does not shift the survey scan m/z values. It shifts the precursor masses before the fragment spectra are associated to their survey scan mass. If you import only *.dta files without a *.csv file, for example, it will mess your data. In this case use MS1 offset.
NOTE: The tolerance settings in LipidXplorer are used as follows: a theoretical mass m measured with a given tolerance a fits to a peak p if <math>m \in [p-a,p+a]</math>.
The same holds for resolution R: two peaks p1 and p2 are considered equal if <math>p_1 \in [p_2-r, p_2+r]</math> where <math>r=\frac{p_1}{R}</math>
store all settings in a configuration
All settings can be stored under a user specified name with Save As .... Save ... saves an already stored setting. Delete deletes a setting. All configurations are stored in the *.ini file which is stated under Select *.ini configurations file. With Browseone can choose another or a new file.
Run queries on the MasterScan
MFQL scripts are used for lipid identification, after the spectra data was imported. Therefore MFQL queries are written in so-called *.mfql files (with the ending *.mfql) where each file should contain just one query. The GUI panel Run is the site where *.mfql files are loaded and run on the MasterScan file.
The Run panel
The big window on the left contains all *.mfql scripts which are used for the lipid identification. This window is managed by the the buttons on its right side:
- Add MFQL File will add one file
- Add MFQL Directory lets you chose a directory containing *.mfql files which are all uploaded.
- Edit MFQL Entry opens an editor panel for the *.mfql entries selected in the left window. Select *.mfql scripts by clicking on it.
- New MFQL Entry opens an editor panel with an empty *.mfql file. A prompt will open and ask you about the name of the file.
- Remove MFQL Entry removes all entries which are selected in the left window.
After choosing your *.mfql files, the MasterScan has to be chosen. This is done by clicking on the green Browse button or by dragging the MasterScan file or the folder in which it is onto the text field. The output file is automatically filled, but can be changed by clicking on the grey Browse button.
Under Optional settings for this run you can change the tolerance settings for the particular run. This option will override the tolerance settings you gave in the Import panel. There, the settings are stored in the MasterScan and used by default, whenever you run this MasterScan. But maybe you want to try another setting, or another and so on, then you can set this here. But the values hold only for this particular run and will not permanently override the settings in the MasterScan.
Isotopic correction for MS and MS/MS can be switched on and off on the lower site of the panel. There is also the option for generation of a complement MasterScan. This is a spectral database containing all entries from the original chosen MasterScan but the identified entries together with their isotopes.
The options No head and Compress change the format of the output slightly. No head removes the head of the output file and Compress removes the names of the queries in the output file. This can be helpful if you want to do some automatic post-processing. The option Tab limited changes the output format from comma separated file format to tab separated file format.
Dump MasterScan lets you write down the content of the MasterScan experimental database to a comma separated file. The MasterScan has its own data format and cannot be viewed by any software. If you want to have a look into it, you need to dump its content into a readable file format. Dump MasterScan will do this in parallel with the Run of your queries, i.e. if you check Dump MasterScan and press Run LipidXplorer the MasterScan will be dumped into a text file (*.csv file format) which you can read out easily with Excel, for example. But MFQL queries are not necessary, to dump the MasterScan.
With Run LipidXplorer the lipid identification is started. The result is saved in the output file. With the View button this file can be viewed on the spot. With View dump file the *.csv file of the MasterScan can be viewed.
The Editor panel
With the editor it is easy to write queries for LipidXplorer. Every query is opened in a separate tab. If a file is edited the Save button changes the color to red to remind the user to save to file before using the query. SaveAs will store the query under a certain file name and Close will close the tab.
The MS-Tools panel
The MS Tools tab contains a small collection of useful functions:
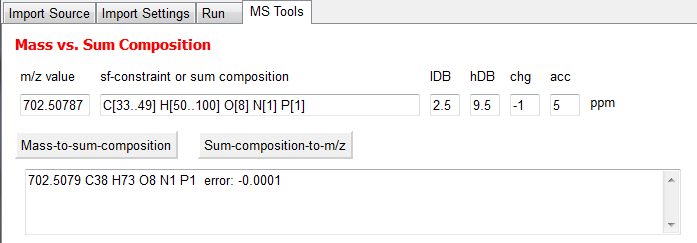
Mass vs. Sum Composition
Calculates either the sum composition out of a given m/z value or the other way round.
Mass-to-sum-composition
Input a m/z value under m/z value and an sc-constraint under sc-constraint or sum composition. lDB is the lower border and hDB the higher border of the double bond equivalent. In chg the charge has to be given and in acc the tolerance value in ppm. Then press Mass-to-sum-composition and the result will be shown in the text window below.
Here an example:
Sum-composition-to-mass
Input a sum composition in sc-constraint or sum composition and a charge in chg. Then press Sum-composition-to-mass and the result will occure in the window below.
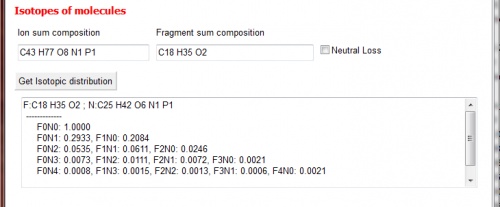
Isotopes of molecules
shows the abundances of the isotopes of a given sum composition. Those values are the ones used in LipidXplorer for isotopic correction. Here the user can double check if everything is working properly.
Isotopic distribution of MS masses
Input a sum composition under Ion sum composition and press Get Isotopic distribution.
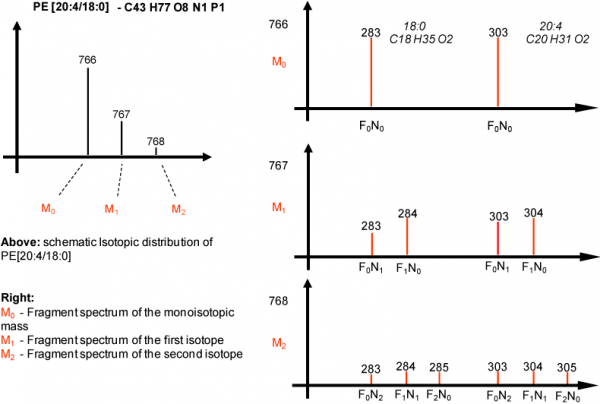
Isotopic distribution of MS/MS masses
The above scheme depicts the values LipidXplorer uses to correct precursor and fragment masses. The isotopes for the fragments are calculated by multiplying the probabilities of fragments (F) having no, one or more than one isotopes with the probabilities of associated neutral losses (N).
For example does F0N0 mean that there is no isotope in the fragment or the neutral loss. F1N0 is the probability of the fragment having one isotope, where the neutral loss has none. The opposite is F0N1 which is the probablility of the fragment containing no isotope because it is contained in the neutral loss.
In MS-Tools the probablities of the isotopes as calculated by LipidXplorer can be viewed. If you put a fragment sum composition in Fragment sum composition the corresponding values are shown in the window below (after pressing Get Isotopic distribution) The mass can either be a real fragment or a neutral loss. This is denoted with the checkbox Neutral Loss.
Store all settings in a project file
You can store all current settings (really all, even the MFQL queries you inserted into the Run Panel) into a file. Re-loading of this file restores all settings. This is done with the Project menu entry:
- Save as ... - to store a new project file
- Save - to re-write the current project file
- Load - to load a project file and restore the settings
Loading a project can be also done by drag'n'drop: Just drop either the project file or the folder in which it is stored over the "Import Panel".
The isotopic correction
The isotopic correction corrects the effects coming from the occurrence of isotopes in the lipid and can be switched on at the Run panel with Isotopic Correction MS and Isotopic Correction MS/MS. LipidXplorer considers two types of isotopic correction (according to [1]):
- The type I correction, corrects the effect of the different isotopic distribution for different numbers of atoms in the molecule. The degree of the type I correction is less than 10% in most cases.
- The type II correction, corrects the effects of overlaps of isotopes containing peaks with another molecular species.
The type II correction is done first to "clean" the spectra from isotopic overlapping effects. Then, the type I correction is done on the identified lipid species.
Type I isotopic correction
For the type I isotopic correction, the sum composition of every identified lipid species is used to calculate its isotopic distribution. The value <math>m</math> of the distribution of the peak with no isotopes is used to correct its intensity by multiplying it with <math>\frac{1}{m}</math>.
Type II isotopic correction
Type II correction for MS
The type II isotopic correction for MS data uses the sum compositions evaluated by LipidXplorer from lipid species and non-lipid species. From the sum compositions the isotopic distribution is calculated. According to this, LipidXplorer detects the isotopes which overlap with detected lipid species and removes the isotopic part of their intensities.
Type II correction for MS/MS
Intrascan isotopic correction
- coming soon ***
Interscan isotopic correction
- coming soon ***
References
[1] Han, X. and Gross, R.W. 2005. Shotgun lipidomics: electrospray ionization mass spectrometric analysis and quantitation of cellular lipidomes directly from crude extracts of biological samples. Mass Spectrom Rev 24(3): 367-412.